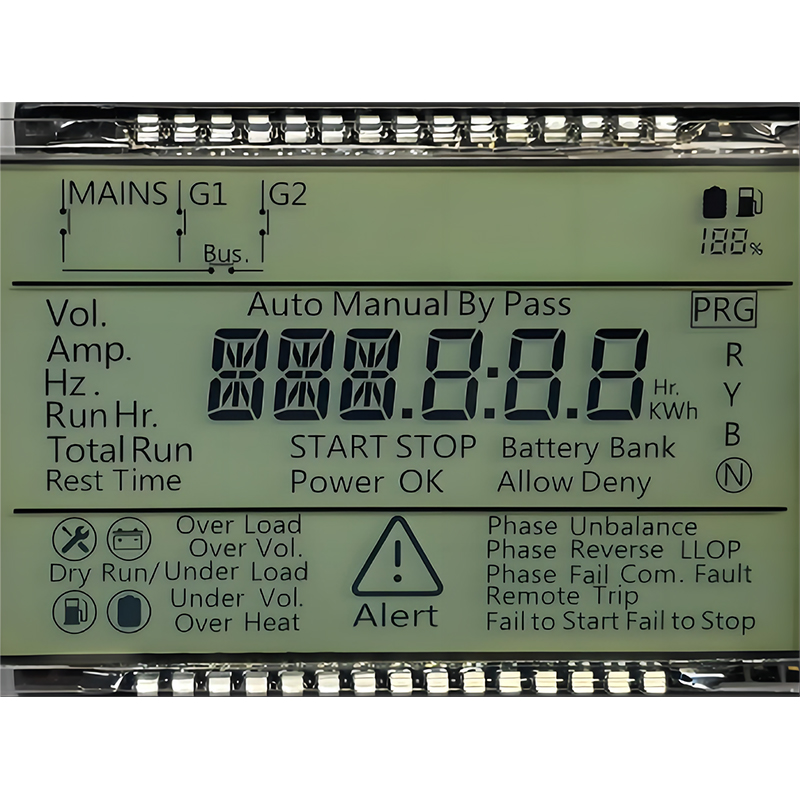
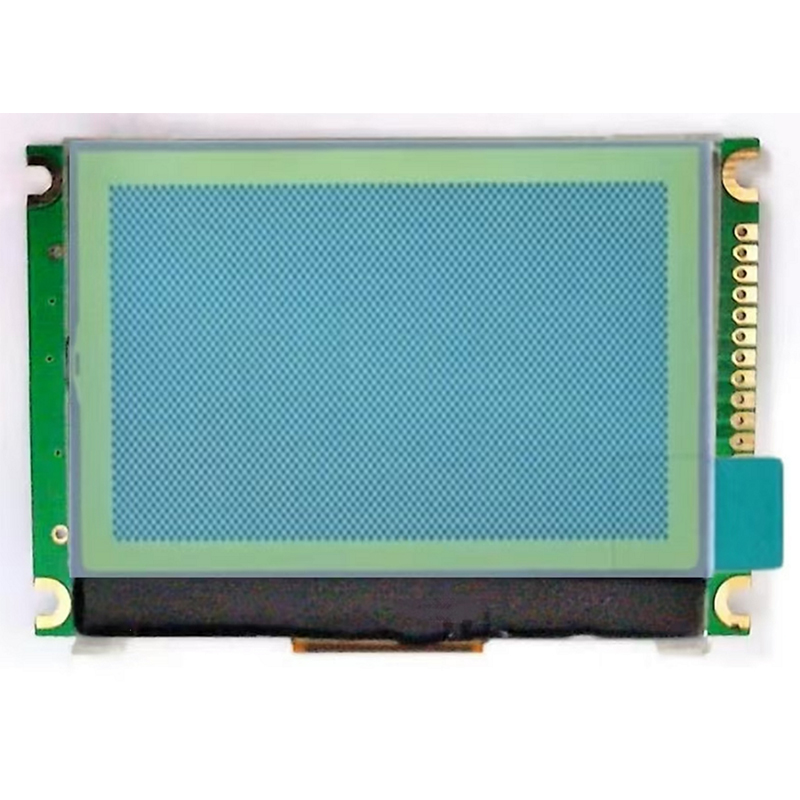
Best Low Power LCD Displays: A Comprehensive GuideThis guide explores the world of low power LCDs, outlining key features, applications, and considerations for selecting the best option for your needs. We'll delve into different technologies, power consumption metrics, and real-world examples to help you make an informed decision.
The demand for energy-efficient displays is constantly growing. Low power LCDs are designed to minimize power consumption without compromising image quality. This is achieved through various technological advancements, including advanced backlight technologies (like edge-lit LED backlights with efficient drivers), optimized driver ICs, and improved display panel technologies themselves. The reduction in power consumption translates directly to longer battery life in portable devices and lower energy bills in stationary applications.
Understanding how power consumption is measured is crucial. Look for specifications like typical operating power (measured in mW), maximum power, and power consumption in different operating modes (e.g., active, sleep, and standby). These metrics will allow for accurate comparisons between different low power LCD models.
Different LCD technologies offer varying levels of power efficiency. For instance, twisted nematic (TN) LCDs are generally less power-hungry than in-plane switching (IPS) LCDs, although IPS offers superior viewing angles. Choosing the right technology depends on your priorities – power efficiency versus image quality and viewing angles.
The backlight significantly impacts power consumption. Edge-lit LED backlights are generally more energy-efficient than traditional CCFL backlights. Advanced backlight control techniques, like local dimming, can further reduce power usage by only illuminating the necessary parts of the screen.
Larger displays with higher resolutions generally consume more power. Consider the optimal size and resolution for your application to balance performance and power efficiency. A smaller, lower-resolution low power LCD might be sufficient for certain applications, significantly reducing power draw.
Various low power LCD types cater to different needs. For example, transflective LCDs are excellent for outdoor applications as they utilize ambient light, reducing the need for a bright backlight. There are also various sizes and form factors available, from tiny displays used in wearable devices to larger displays integrated into industrial equipment. The best choice depends entirely on the application's requirements.
| Technology | Power Consumption | Viewing Angle | Color Reproduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| TN | Low | Narrow | Good |
| IPS | Medium | Wide | Excellent |
| Transflective | Very Low | Wide | Good |
Choosing the optimal low power LCD requires careful consideration of several factors. Understanding your specific application needs, prioritizing key features, and researching available options will lead you to the best solution. For high-quality and reliable low power LCDs, consider exploring options from reputable manufacturers like Dalian Eastern Display Co., Ltd., a leading provider of advanced display solutions.
Remember to always check the manufacturer's specifications for detailed power consumption data and other relevant information.
References: (Add specific links to datasheets and manufacturer websites here as needed)