This comprehensive guide explores the world of I2C LCD displays, covering their functionality, applications, and integration processes. We'll delve into the technical aspects, providing practical examples and troubleshooting tips to empower you to successfully implement these versatile displays in your projects. Learn how to choose the right display, connect it, and program it for optimal performance.
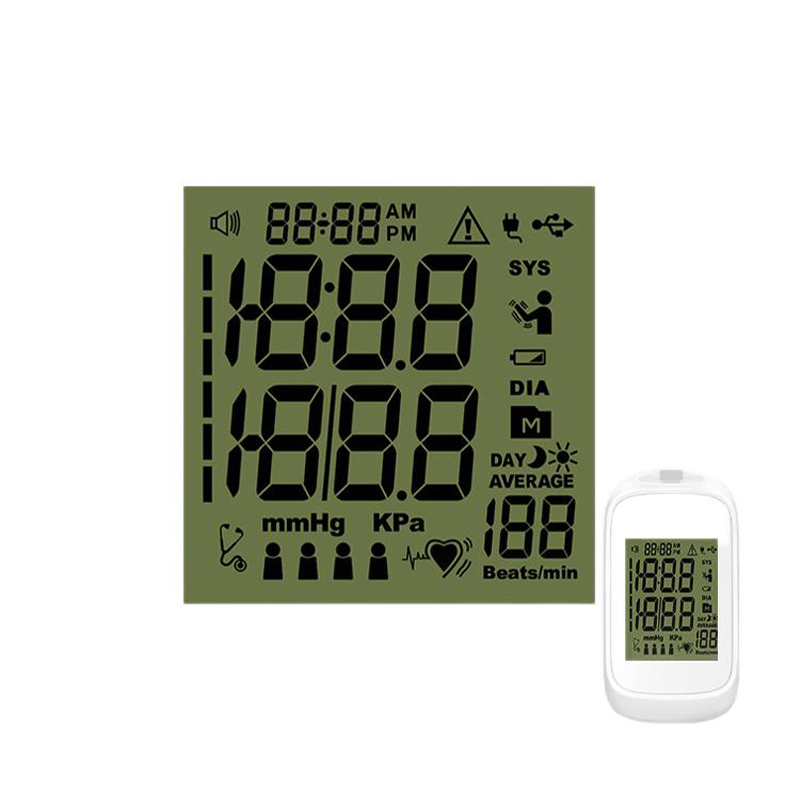
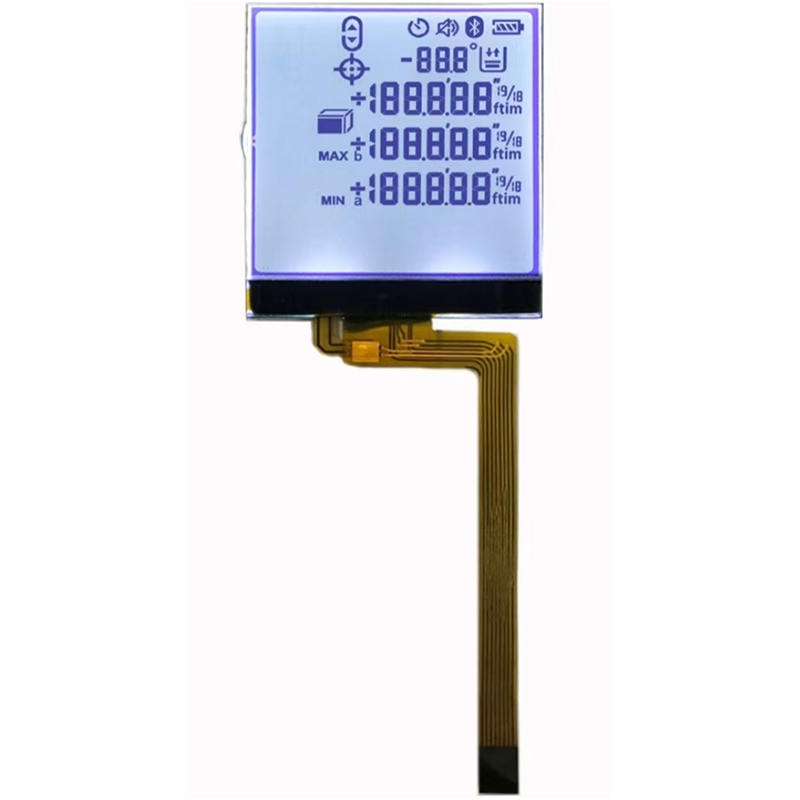
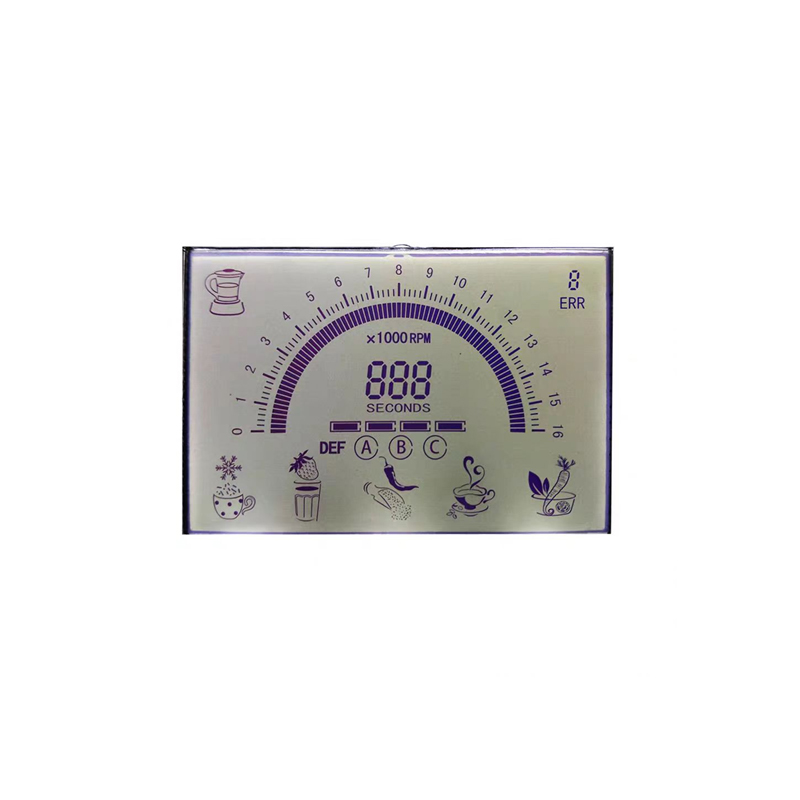
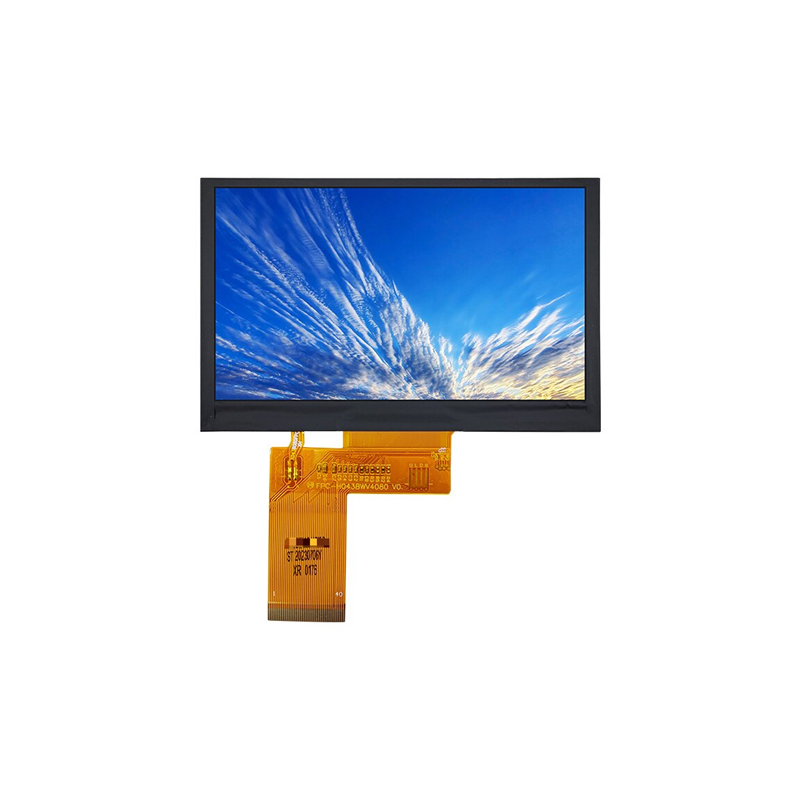
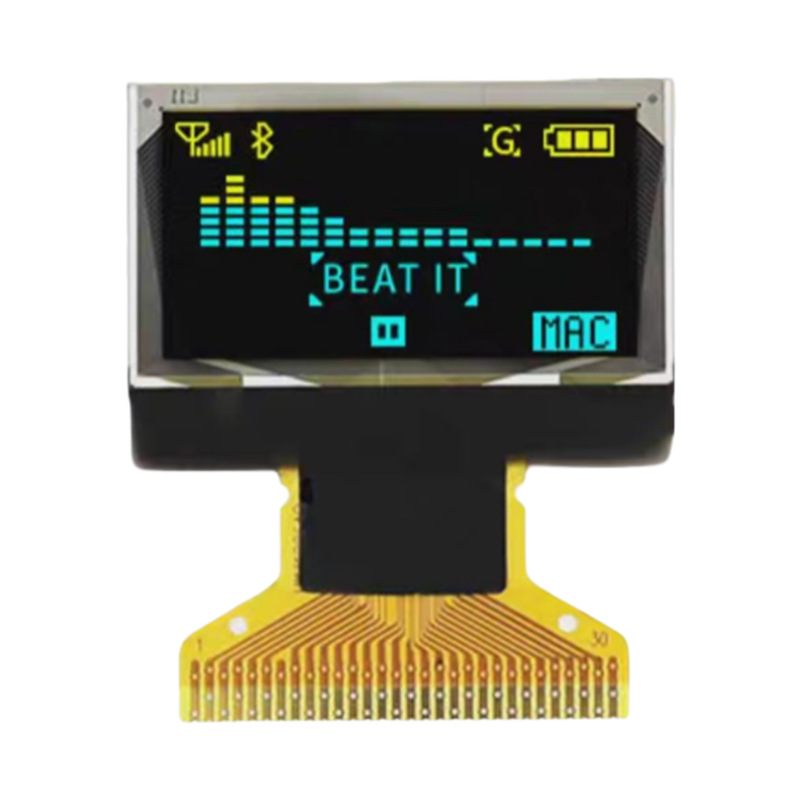
An I2C LCD display is a compact liquid crystal display (LCD) that communicates with a microcontroller or other host device using the I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) protocol. This simplifies the wiring and control compared to other display interfaces, requiring only two data lines (SDA and SCL) for communication, along with power and ground. This makes them incredibly popular for embedded systems and various electronic projects. The displays come in a variety of sizes, resolutions, and functionalities, offering flexibility for different applications. Many offer backlights for improved visibility in low-light conditions.
Understanding the key specifications is crucial for selecting the appropriate I2C LCD display for your project. Consider these factors:
Displays are available in various sizes, ranging from small, single-line displays to larger displays capable of displaying multiple lines of text and even graphics. Resolution, measured in pixels, determines the clarity and detail of the displayed information. Higher resolution generally means sharper images and text, but may increase complexity and power consumption.
The most critical aspect is the interface. While we're focusing on I2C LCD displays, it's important to note that other communication protocols exist (such as SPI and parallel interfaces). I2C's simplicity and ease of use make it a favorite amongst hobbyists and professionals alike.
Backlit displays are essential for readability in dim environments. The type of backlight (e.g., LED) and its intensity can affect power consumption and the overall visual experience. Contrast ratio affects the visibility of the displayed information against the background.
Power consumption is a significant consideration, especially in battery-powered applications. The display's power requirements should be carefully checked and matched with the capabilities of your power source.
The ideal I2C LCD display will depend on your project's specific requirements. Consider factors such as available space, desired resolution, power constraints, and the required functionality. Many reputable suppliers offer a wide range of options; for high-quality displays and excellent customer service, consider exploring options from manufacturers like Dalian Eastern Display Co., Ltd.
Connecting an I2C LCD display is relatively straightforward. You will need to connect the SDA, SCL, VCC (power), and GND (ground) pins to your microcontroller. The specific pin assignments will vary depending on the display model and your microcontroller. Refer to your display's datasheet for the correct wiring.
Programming the display involves using libraries specific to your microcontroller and the display's character set or addressing mode. Many popular microcontroller platforms have readily available libraries to simplify this process. Once connected, you can use the library functions to send commands and data to control what is displayed.
Despite the simplicity of I2C LCD displays, you might encounter some issues. Here are some common problems and their potential solutions:
I2C LCD displays are incredibly versatile components, well-suited for a wide range of embedded systems and projects. Understanding their capabilities and the process of selection, connection, and programming will empower you to create innovative and visually appealing applications.